A) $3
B) $4
C) $5
D) $6
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that two poker players believe that they are superior players to the rest of the people at their table.Further suppose that the two players make an agreement to concede hands to each other in order to drive the other players from the game first.Economists would model such behavior as
A) monopolistic competition.
B) game theory.
C) predatory pricing.
D) a dominant strategy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-5. Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Kunal and Naj, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Kunal and Naj work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump, to bring the water to town, and to sell it at whatever price the market will bear. Assume Kunal and Naj can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero.
The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water are shown in the table below.
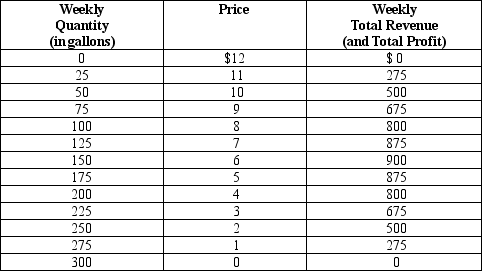 -Refer to Table 17-5.Since Kunal and Naj operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly in the market for water,what price will they charge for water?
-Refer to Table 17-5.Since Kunal and Naj operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly in the market for water,what price will they charge for water?
A) $2
B) $4
C) $6
D) $7
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-12
Each year the United States considers renewal of Most Favored Nation (MFN) trading status with Farland (a mythical nation) . Historically, legislators have made threats of not renewing MFN status because of human rights abuses in Farland. The non-renewal of MFN trading status is likely to involve some retaliatory measures by Farland. The payoff table below shows the potential economic gains associated with a game in which Farland may impose trade sanctions against U.S. firms and the United States may not renew MFN status with Farland. The table contains the dollar value of all trade-flow benefits to the United States and Farland.
 -Refer to Table 17-12.If trade negotiators are able to communicate effectively about the consequences of various trade policies (i.e.,enter into an agreement about the policy they should adopt) ,then we would expect the countries to agree to which outcome?
-Refer to Table 17-12.If trade negotiators are able to communicate effectively about the consequences of various trade policies (i.e.,enter into an agreement about the policy they should adopt) ,then we would expect the countries to agree to which outcome?
A) United States $35 b and Farland $285 b
B) United States $65 b and Farland $75 b
C) United States $140 b and Farland $5 b
D) United States $130 b and Farland $275 b
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predatory pricing involves a firm
A) colluding with another firm to restrict output and raise prices.
B) selling two individual products together for a single price rather than selling each product individually at separate prices.
C) temporarily cutting the price of its product to drive a competitor out of the market.
D) requiring that the firm reselling its product do so at a specified price.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the number of firms in an oligopoly market
A) decreases, the price charged by firms likely decreases.
B) decreases, the market approaches the competitive market outcome.
C) increases, the market approaches the competitive market outcome.
D) increases, the market approaches the monopoly outcome.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) If duopolists successfully collude, then their combined output will be equal to the output that would be observed if the market were a monopoly.
B) Although the logic of self-interest decreases a duopoly's price below the monopoly price, it does not push the duopolists to reach the competitive price.
C) Although the logic of self-interest increases a duopoly's level of output above the monopoly level, it does not push the duopolists to reach the competitive level.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is shown in the table below:
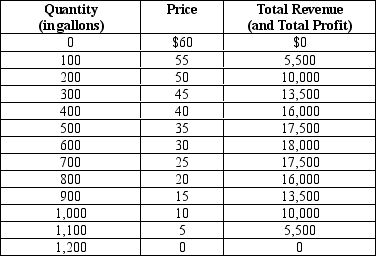 -Refer to Table 17-1.What is the socially efficient quantity of water?
-Refer to Table 17-1.What is the socially efficient quantity of water?
A) 0 gallons
B) 600 gallons
C) 900 gallons
D) 1,200 gallons
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 17-1. Assume that the countries of Irun and Urun are the only two producers of crude oil. Further assume that both countries have entered into an agreement to maintain certain production levels in order to maximize profits. In the world market for oil, the demand curve is downward sloping. -Refer to Scenario 17-1.The fact that both countries have colluded to earn higher profit shows their desire to keep their combined level of output
A) above the monopoly level.
B) below the Nash equilibrium level.
C) equal to the Nash equilibrium level.
D) above the Nash equilibrium level.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-9
Only two firms, Acme and Pinnacle, sell a particular product. The table below shows the demand curve for their product. Each firm has the same constant marginal cost of $10 and zero fixed cost.
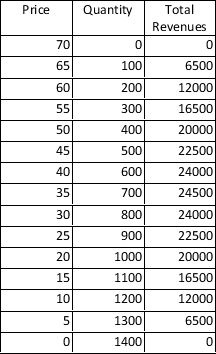 -Refer to Table 17-9.If Acme and Pinnacle operate to jointly maximize profits,then what quantity is sold?
-Refer to Table 17-9.If Acme and Pinnacle operate to jointly maximize profits,then what quantity is sold?
A) 800
B) 700
C) 600
D) 500
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When strategic interactions are important to pricing and production decisions,a typical firm will
A) set the price of its product equal to marginal cost.
B) consider how competing firms might respond to its actions.
C) generally operate as if it is a monopolist.
D) consider exiting the market.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct? When oligopolies collude
A) they make higher profits and consumers of the product are better off.
B) they make higher profits but consumers of the product are worse off.
C) they make lower profits and consumers of the product are better off.
D) they make lower profits and consumers of the product are worse off.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an oligopolist is part of a cartel that is collectively producing the monopoly level of output,then that oligopolist has the incentive to lower production with the aim of
A) lowering prices.
B) increasing profits for the group of firms as a whole.
C) increasing profits for itself, regardless of the impact on profits for the group of firms as a whole.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The essence of an oligopolistic market is that there are only a few sellers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-12
Each year the United States considers renewal of Most Favored Nation (MFN) trading status with Farland (a mythical nation) . Historically, legislators have made threats of not renewing MFN status because of human rights abuses in Farland. The non-renewal of MFN trading status is likely to involve some retaliatory measures by Farland. The payoff table below shows the potential economic gains associated with a game in which Farland may impose trade sanctions against U.S. firms and the United States may not renew MFN status with Farland. The table contains the dollar value of all trade-flow benefits to the United States and Farland.
 -Refer to Table 17-12.If both countries follow a dominant strategy,the value of trade flow benefits for the United States will be
-Refer to Table 17-12.If both countries follow a dominant strategy,the value of trade flow benefits for the United States will be
A) $35 b.
B) $65 b.
C) $275 b.
D) $285 b.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After initial success,the OPEC cartel saw the price of oil and the revenues of its members decline due,in part,to
A) the low elasticity of demand for oil in the short run.
B) the large number of buyers from each member nation.
C) surging demand for oil in the early 1980s.
D) OPEC members failing to produce their agreed-upon production levels.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 17-4. Consider two cigarette companies, PM Inc. and Brown Inc. If neither company advertises, the two companies split the market and earn $50 million each. If they both advertise, they again split the market, but profits are lower by $10 million since each company must bear the cost of advertising. Yet if one company advertises while the other does not, the one that advertises attracts customers from the other. In this case, the company that advertises earns $60 million while the company that does not advertise earns only $30 million. -Refer to Scenario 17-4.If these two companies collude and agree upon the best joint strategy,
A) neither company will advertise.
B) both companies will advertise.
C) PM Inc. will advertise but Brown Inc. will not.
D) Brown Inc. will advertise but PM Inc. will not.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cartels with a small number of firms have a greater probability of reaching the monopoly outcome than do cartels with a larger number of firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium quantity in markets characterized by oligopoly is
A) higher than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
B) higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
C) lower than in monopoly markets and higher than in perfectly competitive markets.
D) lower than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 17-6. The table shows the demand schedule for a particular product.
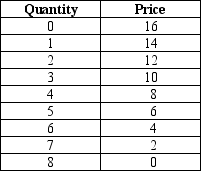 -Refer to Table 17-6.Suppose the market for this product is served by two firms that have formed a cartel.What price will the cartel charge in this market if the marginal cost of production is $0?
-Refer to Table 17-6.Suppose the market for this product is served by two firms that have formed a cartel.What price will the cartel charge in this market if the marginal cost of production is $0?
A) $6
B) $8
C) $10
D) $12
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 410
Related Exams