A) scarcity
B) monetary exchange
C) opportunity cost
D) attainable and unattainable points
E) the tradeoff between producing one good versus another
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As production of food increases, marginal benefit from food
A) increases and marginal cost increases.
B) increases and marginal cost decreases.
C) decreases and marginal cost increases.
D) decreases and marginal cost decreases.
E) decreases and marginal cost is zero.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal benefit curve from a good
A) shows the benefit a firm receives from producing one more unit of that good.
B) shows the most a consumer is willing to pay for one more unit of that good.
C) is upward-sloping.
D) is bowed outward.
E) is vertical.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2.1.1
The following table gives points on the production possibilities frontier for goods X and Y.
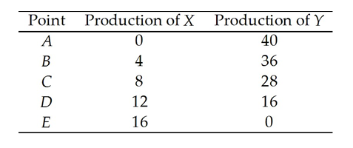 -Refer to Table 2.1.1. As we increase the production of X,
-Refer to Table 2.1.1. As we increase the production of X,
A) the amount of Y that is given up for each additional unit of X decreases.
B) the output of Y increases.
C) the opportunity cost of each additional unit of X increases.
D) unemployment increases.
E) the amount of X increases at an increasing rate.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a graph of a production possibilities frontier, opportunity cost is represented by
A) a point on the horizontal axis.
B) a point on the vertical axis.
C) a ray through the origin.
D) the slope of the production possibilities frontier.
E) the x-axis intercept.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following question.
Table 2.1.4
Consider the following production possibilities for a student for the typical week:
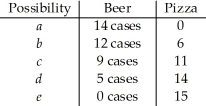 -Refer to Table 2.1.4. Complete the following sentence. The production possibilities frontier in the table shows
-Refer to Table 2.1.4. Complete the following sentence. The production possibilities frontier in the table shows
A) increasing opportunity cost.
B) learning-by-doing.
C) constant opportunity cost.
D) under-utilization of resources.
E) decreasing opportunity cost.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.1.2
Production Possibilities
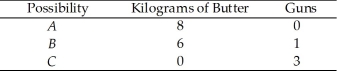 -Refer to Table 2.1.2. In moving from combination B to combination C, the opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of guns is
-Refer to Table 2.1.2. In moving from combination B to combination C, the opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of guns is
A) 2 kilograms of butter.
B) 1/2 kilogram of butter.
C) 6 kilograms of butter.
D) 1/6 kilogram of butter.
E) 3 kilograms of butter.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
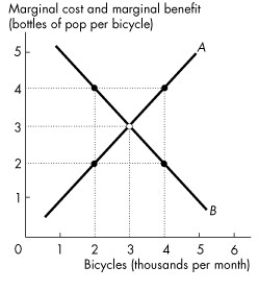 Figure 2.2.1
-In Figure 2.2.1, when 4,000 bicycles are produced each month,
Figure 2.2.1
-In Figure 2.2.1, when 4,000 bicycles are produced each month,
A) the marginal benefit from another bicycle is greater than the marginal cost of another bicycle.
B) more bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
C) fewer bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
D) the economy is efficient at this level of production of bicycles.
E) both A and B.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trade is organized using the social institutions of all of the following except
A) firms.
B) property rights.
C) money.
D) markets.
E) labour unions
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a PPF that measures the production of quilts on the y-axis and the production of pillows on the x-axis. As the firm moves along this PPF, the quantities of
A) all goods other than pillows and quilts are decreasing.
B) all goods other than pillows and quilts remain constant.
C) all goods other than pillows and quilts are increasing.
D) pillows and quilts produced increase together.
E) pillows and quilts produced decrease together.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following quotations illustrates economic growth?
A) "The firm should lower the price it charges for widgets and gadgets."
B) "The firm should sell more gadgets, even if it means less widget sales."
C) "The more and more gadgets the firm produces, the bigger the fall in widget production."
D) "If the firm invests more in capital equipment, it can expand production next year."
E) "The firm has been able to lower costs due to its extensive experience in building widgets."
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
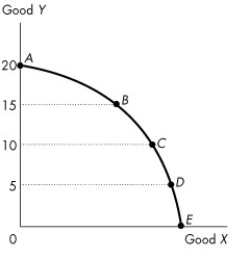 Figure 2.1.3
-Figure 2.1.3 illustrates Mary's production possibilities frontier. If Mary wants to move from point B to point C,
Figure 2.1.3
-Figure 2.1.3 illustrates Mary's production possibilities frontier. If Mary wants to move from point B to point C,
A) it will be necessary to improve technology.
B) it will be necessary to increase the accumulation of capital.
C) it will be necessary to give up some of good X to obtain more of good Y.
D) it will be necessary to give up some of good Y to obtain more of good X.
E) she can accomplish this without any opportunity cost.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 2.1.3
-Refer to the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.3. The opportunity cost of moving from C to B will be
Figure 2.1.3
-Refer to the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.3. The opportunity cost of moving from C to B will be
A) greater than moving from D to C but less than moving from B to A.
B) less than moving from D to C but greater than moving from B to A.
C) the same as moving from D to C or moving from B to A.
D) greater than moving either from D to C or from B to A.
E) less than moving from E to D.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information below to answer the following questions. Fact 2.4.2 Agnes can produce either 1 unit of X or 1 unit of Y in an hour, while Brenda can produce either 2 units of X or 4 units of Y in an hour. -Complete the following sentence. Given Fact 2.4.2,
A) there will be gains from trade, no matter what Brenda and Agnes specialize in, as long as they specialize.
B) there will be gains from trade only if Agnes specializes in the production of Y and Brenda in X.
C) there will be gains from trade only if Agnes becomes faster at producing X.
D) there will be no gains from trade because Agnes has an absolute advantage.
E) there will be gains from trade if Agnes specializes in the production of X and Brenda in Y.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 2.2.1
-In Figure 2.2.1, when 2,000 bicycles are produced each month,
Figure 2.2.1
-In Figure 2.2.1, when 2,000 bicycles are produced each month,
A) the marginal benefit from another bicycle is greater than the marginal cost of another bicycle.
B) more bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
C) fewer bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
D) the economy is efficient at this level of production of bicycles.
E) both A and B.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
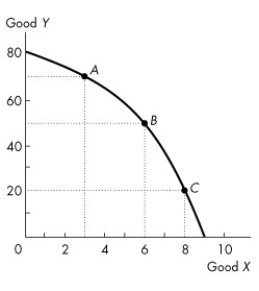 Figure 2.1.2
-Consider the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.2. Which of the following statements is false?
Figure 2.1.2
-Consider the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.2. Which of the following statements is false?
A) Resources are not equally useful in all activities.
B) Points inside the production possibilities frontier indicate unused or misallocated resources.
C) Starting at point A, an increase in the production of Y will shift the production possibilities frontier outward.
D) The opportunity cost of producing Y increases as production of Y increases.
E) The opportunity cost of producing X increases as production of X increases.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A situation in which resources are either unused or misallocated or both is represented in a production possibilities frontier diagram by
A) any point on either the horizontal or the vertical axis.
B) a point above or to the right of the production possibilities frontier.
C) a point outside the production possibilities frontier.
D) a point inside the production possibilities frontier.
E) a point on or inside the production possibilities frontier.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.4.2
Production for one week by Sheila and Bruce
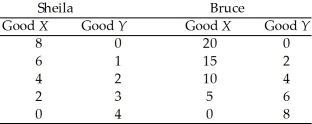 -Given the information in Table 2.4.2, can Sheila and Bruce gain by specialization?
-Given the information in Table 2.4.2, can Sheila and Bruce gain by specialization?
A) Yes, but only if Bruce gets paid more than Sheila.
B) No, not under the given circumstances.
C) It depends on the wages each earns.
D) Only if they are married to each other.
E) Yes, if each specializes in the good in which he has a comparative advantage.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier will shift outward FOR ALL OF THE FOLLOWING REASONS EXCEPT
A) a technological improvement.
B) an increase in the stock of capital.
C) an increase in the labour force.
D) an increase in opportunity cost.
E) an increase in human capital.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 159 of 159
Related Exams