A) 2.08%
B) 2.31%
C) 2.57%
D) 2.82%
E) 3.10%
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Normal Projects S and L have the same NPV when the discount rate is zero.However, Project S's cash flows come in faster than those of L.Therefore, we know that at any discount rate greater than zero, L will have the higher NPV.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects S and L, whose cash flows are shown below, are mutually exclusive, equally risky, and not repeatable.Hooper Inc.is considering which of these two projects to undertake.If the decision is made by choosing the project with the higher IRR, how much value will be forgone? Note that under certain conditions choosing projects on the basis of the IRR will not cause any value to be lost because the project with the higher IRR will also have the higher NPV, so no value will be lost if the IRR method is used.
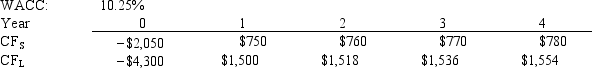
A) $134.79
B) $141.89
C) $149.36
D) $164.29
E) $205.36
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Shannon Co.is considering a project that has the following cash flow and WACC data.What is the project's discounted payback?

A) 1.61 years
B) 1.79 years
C) 1.99 years
D) 2.22 years
E) 2.44 years
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Current Design Co.is considering two mutually exclusive, equally risky, and not repeatable projects, S and L.Their cash flows are shown below.The CEO believes the IRR is the best selection criterion, while the CFO advocates the NPV.If the decision is made by choosing the project with the higher IRR rather than the one with the higher NPV, how much, if any, value will be forgone, i.e., what's the chosen NPV versus the maximum possible NPV? Note that (1) "true value" is measured by NPV, and (2) under some conditions the choice of IRR vs.NPV will have no effect on the value gained or lost.
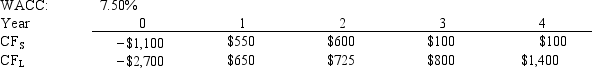
A) $138.10
B) $149.21
C) $160.31
D) $171.42
E) $182.52
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clifford Company is choosing between two projects.The larger project has an initial cost of $100, 000, annual cash flows of $30, 000 for 5 years, and an IRR of 15.24%.The smaller project has an initial cost of $50, 000, annual cash flows of $16, 000 for 5 years, and an IRR of 16.63%.The projects are equally risky.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the larger project will look better based on the NPV at all positive values of WACC.
B) If the company uses the NPV method, it will tend to favor smaller, shorter-term projects over larger, longer-term projects, regardless of how high or low the WACC is.
C) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR but the larger project has the higher NPV at a zero discount rate, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the larger project will have the higher NPV if the WACC is less than the crossover rate.
D) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR and the larger NPV at a zero discount rate, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the smaller project will look better if the WACC is less than the crossover rate.
E) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR, the two projects' NPV profiles cannot cross, and the smaller project's NPV will be higher at all positive values of WACC.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In theory, capital budgeting decisions should depend solely on forecasted cash flows and the opportunity cost of capital.The decision criterion should not be affected by managers' tastes, choice of accounting method, or the profitability of other independent projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a project has normal cash flows.All else equal, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) A project's NPV increases as the WACC declines.
B) A project's MIRR is unaffected by changes in the WACC.
C) A project's regular payback increases as the WACC declines.
D) A project's discounted payback increases as the WACC declines.
E) A project's IRR increases as the WACC declines.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 108 of 108
Related Exams