A) The firm's corporate,or overall,WACC is used to discount all project cash flows to find the projects' NPVs.Then,depending on how risky different projects are judged to be,the calculated NPVs are scaled up or down to adjust for differential risk.
B) Differential project risk cannot be accounted for by using "risk-adjusted discount rates" because it is highly subjective and difficult to justify.It is better to not risk adjust at all.
C) Other things held constant,if returns on a project are thought to be positively correlated with the returns on other firms in the economy,then the project's NPV will be found using a lower discount rate than would be appropriate if the project's returns were negatively correlated.
D) Monte Carlo simulation uses a computer to generate random sets of inputs,those inputs are then used to determine a trial NPV,and a number of trial NPVs are averaged to find the project's expected NPV.Sensitivity and scenario analyses,on the other hand,require much more information regarding the input variables,including probability distributions and correlations among those variables.This makes it easier to implement a simulation analysis than a scenario or sensitivity analysis,hence simulation is the most frequently used procedure.
E) DCF techniques were originally developed to value passive investments (stocks and bonds) .However,capital budgeting projects are not passive investments - managers can often take positive actions after the investment has been made that alter the cash flow stream.Opportunities for such actions are called real options.Real options are valuable,but this value is not captured by conventional NPV analysis.Therefore,a project's real options must be considered separately.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Typically,a project will have a higher NPV if the firm immediately expenses depreciation rather than using straight-line depreciation.This is because the total cash flows over the project's life will be higher if depreciation is immediately expensed,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors should be included in the cash flows used to estimate a project's NPV?
A) All costs associated with the project that have been incurred prior to the time the analysis is being conducted.
B) Interest on funds borrowed to help finance the project.
C) The end-of-project recovery of any additional net operating working capital required to operate the project.
D) Cannibalization effects,but only if those effects increase the project's projected cash flows.
E) Expenditures to date on research and development related to the project,provided those costs have already been expensed for tax purposes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In cash flow estimation,the existence of externalities should be taken into account if those externalities have any effects on the firm's long-run cash flows.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liberty Services is now at the end of the final year of a project.The equipment was purchased prior to the new tax law and originally cost $20,000,of which 75% has been depreciated.The firm can sell the used equipment today for $6,000,and its tax rate is 25%.What is the equipment's after-tax salvage value for use in a capital budgeting analysis? Note that if the equipment's final market value is less than its book value,the firm will receive a tax credit as a result of the sale that will offset income from the company's other projects.
A) $5,750
B) $5,060
C) $5,335
D) $4,180
E) $6,380
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is extremely difficult to estimate the revenues and costs associated with large,complex projects that take several years to develop.This is why subjective judgment is often used for such projects along with discounted cash flow analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sub-Prime Loan Company is thinking of opening a new office,and the key data are shown below.The company owns the building that would be used,and it could sell it for $100,000 after taxes if it decides not to open the new office.Under the new tax law,the equipment used in the project is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.At the end of the project's life,the equipment would have zero salvage value.No change in net operating working capital (NOWC) would be required for the project.Revenues and operating costs would be constant over the project's 3-year life.What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Cash flows are constant in Years 1-3. ) Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number. 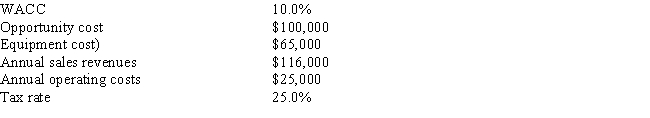
A) $20,978
B) $36,761
C) $18,450
D) $34,900
E) $12,543
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Taussig Technologies is considering two potential projects,X and Y.In assessing the projects' risks,the company estimated the beta of each project versus both the company's other assets and the stock market,and it also conducted thorough scenario and simulation analyses.This research produced the following data: Which of the following statements is CORRECT?

A) Project X has more stand-alone risk than Project Y.
B) Project X has more corporate (or within-firm) risk than Project Y.
C) Project X has more market risk than Project Y.
D) Project X has the same level of corporate risk as Project Y.
E) Project X has the same market risk as Project Y since its cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows of existing projects.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm is considering a new project whose risk is greater than the risk of the firm's average project,based on all methods for assessing risk.In evaluating this project,it would be reasonable for management to do which of the following?
A) Increase the estimated IRR of the project to reflect its greater risk.
B) Increase the estimated NPV of the project to reflect its greater risk.
C) Reject the project,since its acceptance would increase the firm's risk.
D) Ignore the risk differential if the project would amount to only a small fraction of the firm's total assets.
E) Increase the cost of capital used to evaluate the project to reflect its higher-than-average risk.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two cardinal rules that financial analysts should follow to avoid errors are: (1)in the NPV equation,the numerator should use income calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,and (2)all incremental cash flows should be considered when making accept/reject decisions for capital budgeting projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You work for Whittenerg Inc. ,which is considering a new project whose data are shown below.Under the new tax law,the equipment used in the project is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.What is the project's Year 1 cash flow? 
A) $22,849
B) $26,149
C) $32,063
D) $20,818
E) $30,211
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because of improvements in forecasting techniques,estimating the cash flows associated with a project has become the easiest step in the capital budgeting process.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since depreciation is a cash expense,the faster an asset is depreciated,the lower the projected NPV from investing in the asset.
B) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
C) Corporations must use the same depreciation method for both stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
D) Using bonus depreciation rather than straight line normally has the effect of receiving depreciation cash flows immediately and thus increasing a project's forecasted NPV.
E) Using bonus depreciation rather than straight line normally has the effect of delaying the receipt of depreciation cash flows and thus reducing a project's forecasted NPV.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any cash flows that can be classified as incremental to a particular project--i.e. ,results directly from the decision to undertake the project--should be reflected in the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clemson Software is considering a new project whose data are shown below.The required equipment has a 3-year tax life,after which it will be worthless.Under the new tax law,the equipment is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.Revenues and operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life.What is the project's Year 1 cash flow? Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number. 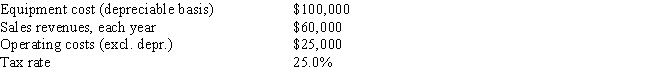
A) $33,040
B) $32,008
C) $29,598
D) $28,222
E) $26,250
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company is considering a proposed new plant that would increase productive capacity.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) In calculating the project's operating cash flows,the firm should not deduct financing costs such as interest expense,because financing costs are accounted for by discounting at the WACC.If interest were deducted when estimating cash flows,this would,in effect,"double count" it.
B) Since depreciation is a non-cash expense,it has no impact on a project's calculated NPV..
C) When estimating the project's operating cash flows,it is important to include both opportunity costs and sunk costs,but the firm should ignore the cash flow effects of externalities since they are accounted for in the discounting process.
D) Capital budgeting decisions should be based on before-tax cash flows because WACC is calculated on a before-tax basis.
E) The WACC used to discount cash flows in a capital budgeting analysis should be calculated on a before-tax basis.To do otherwise would bias the NPV upward.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a relevant cash flow and thus should NOT be reflected in the analysis of a capital budgeting project?
A) Changes in net operating working capital.
B) Shipping and installation costs for machinery acquired.
C) Cannibalization effects.
D) Opportunity costs.
E) Sunk costs that have been expensed for tax purposes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a member of UA Corporation's financial staff,you must estimate the Year 1 cash flow for a proposed project with the following data.Under the new tax law,the equipment used in the project is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.What is the Year 1 cash flow? Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number. 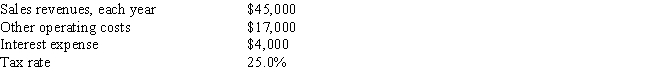
A) $22,922
B) $17,677
C) $20,785
D) $21,375
E) $17,871
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since depreciation is not a cash expense,and since cash flows and not accounting income are the relevant input,depreciation plays no role in capital budgeting.
B) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 3 years or longer.
C) If firms use bonus depreciation,they will write off assets slower than they would under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVswould normally be lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes..
D) If firms use bonus depreciation,they can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs would normally be lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
E) If firms use bonus depreciation,they can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs would normally be higher than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following should be considered when a company estimates the cash flows used to analyze a proposed project?
A) The new project is expected to reduce sales of one of the company's existing products by 5%.
B) Since the firm's director of capital budgeting spent some of her time last year to evaluate the new project,a portion of her salary for that year should be charged to the project's initial cost.
C) The company has spent and expensed $1 million on research and development costs associated with the new project.
D) The company spent and expensed $10 million on a marketing study before its current analysis regarding whether to accept or reject the project.
E) The firm would borrow all the money used to finance the new project,and the interest on this debt would be $1.5 million per year.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 73
Related Exams