A) $2,549
B) $18,970
C) $4,571
D) $20,001
E) $1,348
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marshall-Miller & Company is considering the purchase of a new machine for $50,000,installed.The machine has a tax life of 5 years.Under the new tax law,the machine is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.The firm expects to operate the machine for 4 years and then to sell it for $21,500.If the marginal tax rate is 25%,what will the after-tax salvage value be when the machine is sold at the end of Year 4?
A) $12,551
B) $12,877
C) $12,225
D) $16,125
E) $14,833
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Changes in net operating working capital should not be reflected in a capital budgeting cash flow analysis because capital budgeting relates to fixed assets,not working capital.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a firm's projects differ in risk,then one way of handling this problem is to evaluate each project with the appropriate risk-adjusted discount rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fool Proof Software is considering a new project whose data are shown below.The equipment that would be used has a 3-year tax life.Under the new tax law,the equipment used in the project is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.Revenues and operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 10-year expected life.What is the Year 1 cash flow? 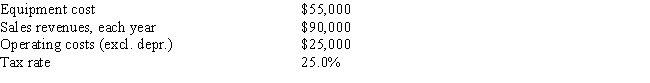
A) $33,177
B) $22,409
C) $48,750
D) $26,483
E) $22,991
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sensitivity analysis measures a project's stand-alone risk by showing how much the project's NPV (or IRR)is affected by a small change in one of the input variables,say sales.Other things held constant,with the size of the independent variable graphed on the horizontal axis and the NPV on the vertical axis,the steeper the graph of the relationship line,the more risky the project,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Tapley Inc.uses a WACC of 8% for below-average risk projects,10% for average-risk projects,and 12% for above-average risk projects.Which of the following independent projects should Tapley accept,assuming that the company uses the NPV method when choosing projects?
A) Project A,which has average risk and an IRR = 9%.
B) Project B,which has below-average risk and an IRR = 8.5%.
C) Project C,which has above-average risk and an IRR = 11%.
D) Without information about the projects' NPVs we cannot determine which one or ones should be accepted.
E) All of these projects should be accepted as they will produce a positive NPV.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An example of a sunk cost is the cost associated with restoring the site of a strip mine once the ore has been depleted.
B) Sunk costs must be considered if the IRR method is used but not if the firm relies on the NPV method.
C) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where a bank opens a new office,and that new office leads to a decline in deposits of the bank's other offices.
D) A good example of a sunk cost is money that a banking corporation spent last year to investigate the site for a new office,then expensed that cost for tax purposes,and now is deciding whether to go forward with the project.
E) If sunk costs are considered and reflected in a project's cash flows,then the project's calculated NPV will be higher than it otherwise would have been had the sunk costs been ignored.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) A sunk cost is any cost that must be expended in order to complete a project and bring it into operation.
B) A sunk cost is any cost that was expended in the past but can be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
C) A sunk cost is a cost that was incurred and expensed in the past and cannot be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project.
D) Sunk costs were formerly hard to deal with,but once the NPV method came into wide use,it became possible to simply include sunk costs in the cash flows and then calculate the project's NPV.
E) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where Home Depot opens a new store,and that leads to a decline in sales of one of the firm's existing stores.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The change in net operating working capital (NOWC)associated with new projects is always positive,because new projects mean that more operating working capital will be required.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Florida Car Wash is considering a new project whose data are shown below.The equipment to be used has a 3-year tax life.Under the new tax law,the equipment is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation,so it will be fully depreciated at t = 0.At the end of the project's 3-year life,it would have zero salvage value.No change in net operating working capital (NOWC) would be required for the project.Revenues and operating costs will be constant over the project's life,and this is just one of the firm's many projects,so any losses on it can be used to offset profits in other units.If the number of cars washed declined by 40% from the expected level,by how much would the project's NPV change? (Hint: Note that cash flows are constant at the Year 1 level,whatever that level is. ) Do not round the intermediate calculations and round the final answer to the nearest whole number.
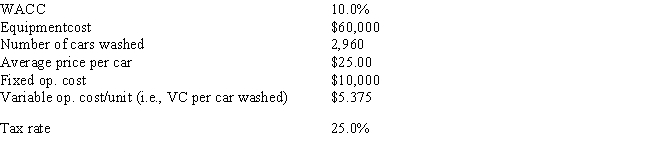
A) -$43,339
B) -$33,804
C) -$28,170
D) -$46,199
E) -$36,433
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If debt is to be used to finance a project,then when cash flows for a project are estimated,interest payments should be included in the analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Although it is extremely difficult to make accurate forecasts of the revenues that a project will generate,projects' initial outlays and subsequent costs can be forecasted with great accuracy.This is especially true for large product development projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) ![]()
B) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
C) Corporations must use the same depreciation method (e.g. ,straight line or accelerated) for stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
D) Since depreciation is not a cash expense,it has no effect on cash flows and thus no effect on capital budgeting decisions.
E) Under bonus depreciation,higher depreciation charges occur at t = 0,and this increases the initial investment outlay and thus lowers a project's projected NPV.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a firm's CFO thinks that an externality is present in a project,but that it cannot be quantified with any precision--estimates of its effect would really just be guesses.In this case,the externality should be ignored--i.e. ,not considered at all--because if it were considered it would make the analysis appear more precise than it really is.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rowell Company spent $3 million two years ago to build a plant for a new product.It then decided not to go forward with the project,so the building is available for sale or for a new product.Rowell owns the building free and clear--there is no mortgage on it.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since the building has been paid for,it can be used by another project with no additional cost.Therefore,it should not be reflected in the cash flows of the capital budgeting analysis for any new project.
B) If the building could be sold,then the after-tax proceeds that would be generated by any such sale should be charged as a cost to any new project that would use it.
C) This is an example of an externality,because the very existence of the building affects the cash flows for any new project that Rowell might consider.
D) Since the building was built in the past,its cost is a sunk cost and thus need not be considered when new projects are being evaluated,even if it would be used by those new projects.
E) If there is a mortgage loan on the building,then the interest on that loan would have to be charged to any new project that used the building.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Opportunity costs include those cash inflows that could be generated from assets the firm already owns if those assets are not used for the project being evaluated.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relative risk of a proposed project is best accounted for by which of the following procedures?
A) Adjusting the discount rate upward if the project is judged to have above-average risk.
B) Adjusting the discount rate upward if the project is judged to have below-average risk.
C) Reducing the NPV by 10% for risky projects.
D) Picking a risk factor equal to the average discount rate.
E) Ignoring risk because project risk cannot be measured accurately.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When evaluating a new project,firms should include in the projected cash flows all of the following EXCEPT:
A) Changes in net operating working capital attributable to the project.
B) Previous expenditures associated with a market test to determine the feasibility of the project,provided those costs have been expensed for tax purposes.
C) The value of a building owned by the firm that will be used for this project.
D) A decline in the sales of an existing product,provided that decline is directly attributable to this project.
E) The salvage value of assets used for the project that will be recovered at the end of the project's life.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Superior analytical techniques,such as NPV,used in combination with risk-adjusted cost of capital estimates,can overcome the problem of poor cash flow estimation and lead to generally correct accept/reject decisions for capital budgeting projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 73
Related Exams